Controlling
Network Security Information
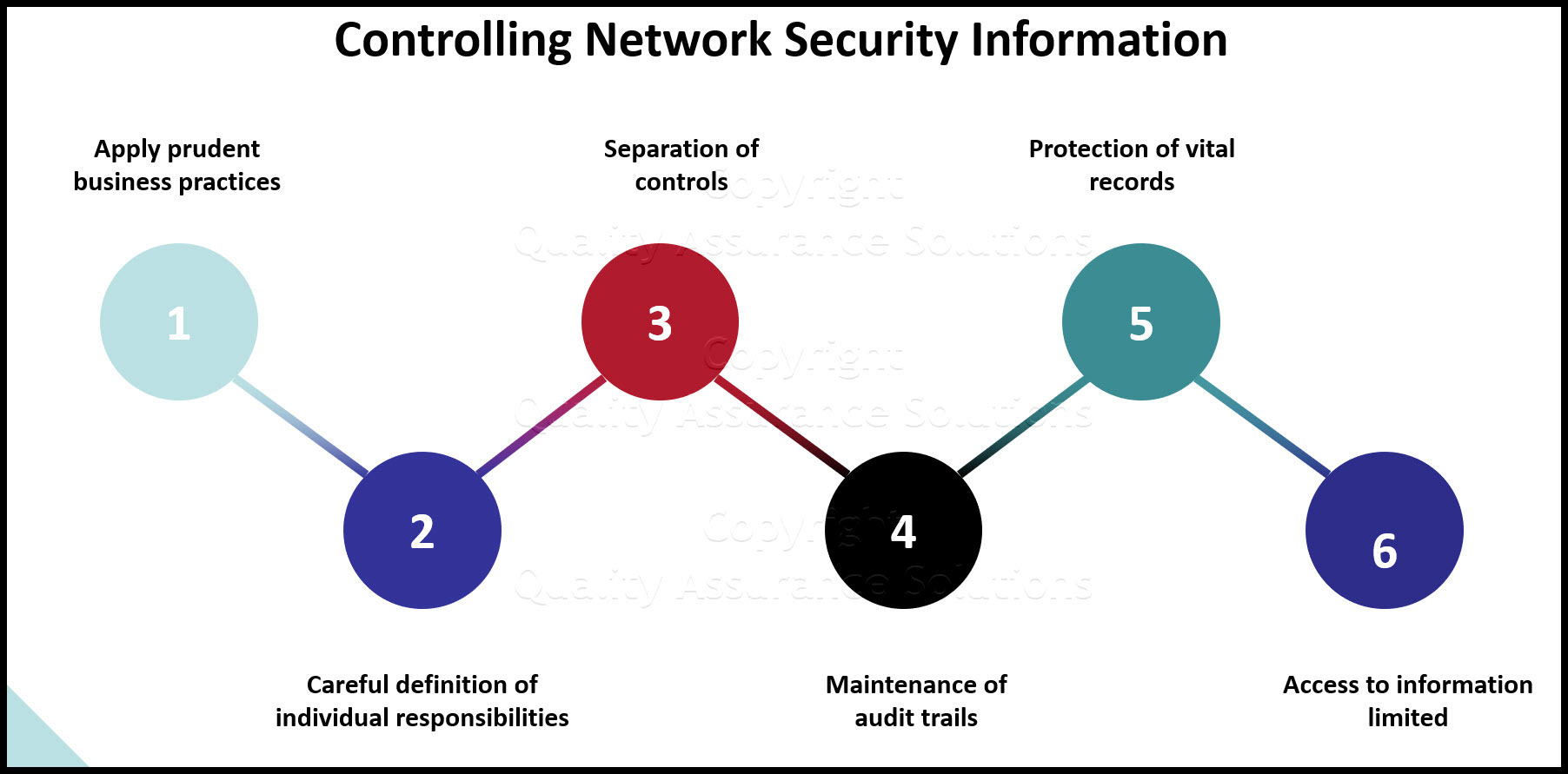
Controlling network security information includes
- applying prudent business practices similar to earlier manual systems (prior to IT)
- careful definition of individual responsibilities
- separation of controls
- maintenance of audit trails
- protection of vital records
- access to information limited, based on "need-to-know"
The actual recipe consists of just (2) fundamental ingredients: IT Policy and Information Security Awareness.
TrainingKeeper Software. Keep, organize and plan all your employees' training and activities. Software includes multi-user support with reports, certs, and calendars.
IT Policy and Network Security Information
Let's take a look at the first ingredient... IT Policy. We base IT Policy on the three sides of a triangle where the three triangle legs consist of: Information Security, Business Continuity, and IT Compliance. Each one of these legs / sides can be broken down / defined as follows:
The Information Security leg consists of confidentiality and integrity. Confidentiality ensures that company / customer information is not disclosed to anyone not authorized to access it. Linked to this concept is the idea of need-to-know, authorizing access only to those who can demonstrate a legitimate business need for the information. Integrity ensures that information cannot be accidentally or intentionally modified or destroyed.
The Business Continuity leg consists of mitigation, crisis management, and contingency management.
- Mitigation deals with reducing or eliminating risks.
- Crisis management deals with the planning and training of people for the survival of the business team and the business entity following a disaster.
- Contingency management deals with planning for the recovery and continuation of critical internal and customer business functions following a service interruption, and the testing of business recovery plans.
Finally, the IT Compliance leg consists of practices that do not fall within the scope of the other two legs. This Includes adherence to the laws and ethics that govern us, i.e., copyright infringement, software licensing, export compliance, etc.
Auditors look for these controls, laws, and / or ethics principles. IT Compliance means passing a stringent audit because the business controls and protects network security information and does not violate any laws.
A published high-level IT Policy must touch on each of these major components in order for the security policy of the IT environment to be all encompassing. Following the high-level definition you need statements that specifically address in detail, the requirements (how the organization accomplishes the high-level definition).
Finally, to make it all happen, you need to implement controls, standards, procedures, and mechanisms to support the policy.
Employee Handbook Kit includes two Employee Handbook templates for Professional & Manufacturing. Includes over 60 policies and benefits templates.
Information Security Awareness
The second ingredient of controlling network security information, means implement Information Security Awareness.
As a primary corporate obligation, companies must protect corporate information, and customer information.
Every employee must understand the corporation's concern with network security information. It is management's responsibility to ensure that all personnel are made aware of pertinent practices, and the requirement to understand and heed them.
Both federal and state regulations exist, which relate to control of, and authorized access to, information and computer resources:
- The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) of 1977 made most corporate managers and directors personally liable for assuring that "transactions are properly authorized, transactions are properly recorded, and access to assets is properly controlled". The Act also requires management to provide shareholders with reasonable assurances that accurate books and records are properly maintained, and that the business is adequately controlled.
- The Copyright Act of 1976 reaffirmed that computer programs and software are protected under the Federal Copyright Law. One must read and understand licensing agreements before attempting to make copies of programs or documentation.
- All of the United States have enacted Computer Crime Laws which establish specific penalties for unauthorized persons attempting to access a computer system, or assisting someone in gaining unauthorized access to a computer system.
|
Quality Assurance Solutions Robert Broughton (805) 419-3344 USA |
 |
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications | ||
|
450+ Editable Slides with support links | ||
|
Corrective Action Software | ||
|
Plan and Track Training | ||
|
AQL Inspection Software |
|
Learn and Train TRIZ | ||
|
Editable Template | ||
|
Templates, Guides, QA Manual, Audit Checklists | ||
|
EMS Manual, Procedures, Forms, Examples, Audits, Videos | ||
|
On-Line Accredited Certifications Six Sigma, Risk Management, SCRUM | ||
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications |