IT Audit Tool and Guide
This article covers IT Audit Tool and Guide. It provides items to review during the audit and question to ask.
IT Audit Tool Scope
Under normal circumstances auditors conduct IT type audits to inspect and to ensure that the company adequately protects information.
With respect to these audits, inspection of the following items would appear to be reasonable:
- Controls regarding access to buildings and sensitive areas
- Controls regarding access to resources (network, system, applications, data) during information creation, transmittal, storage, backup, archival, recovery or restoration, and disposal
- Controls regarding identification and authentication, including inactive session limits, thresholds for maximum sign-on attempts, and password change controls
- Logs of unauthorized and unsuccessful attempts to access applications and information
- Controls related to malicious software (virus’s & worms)
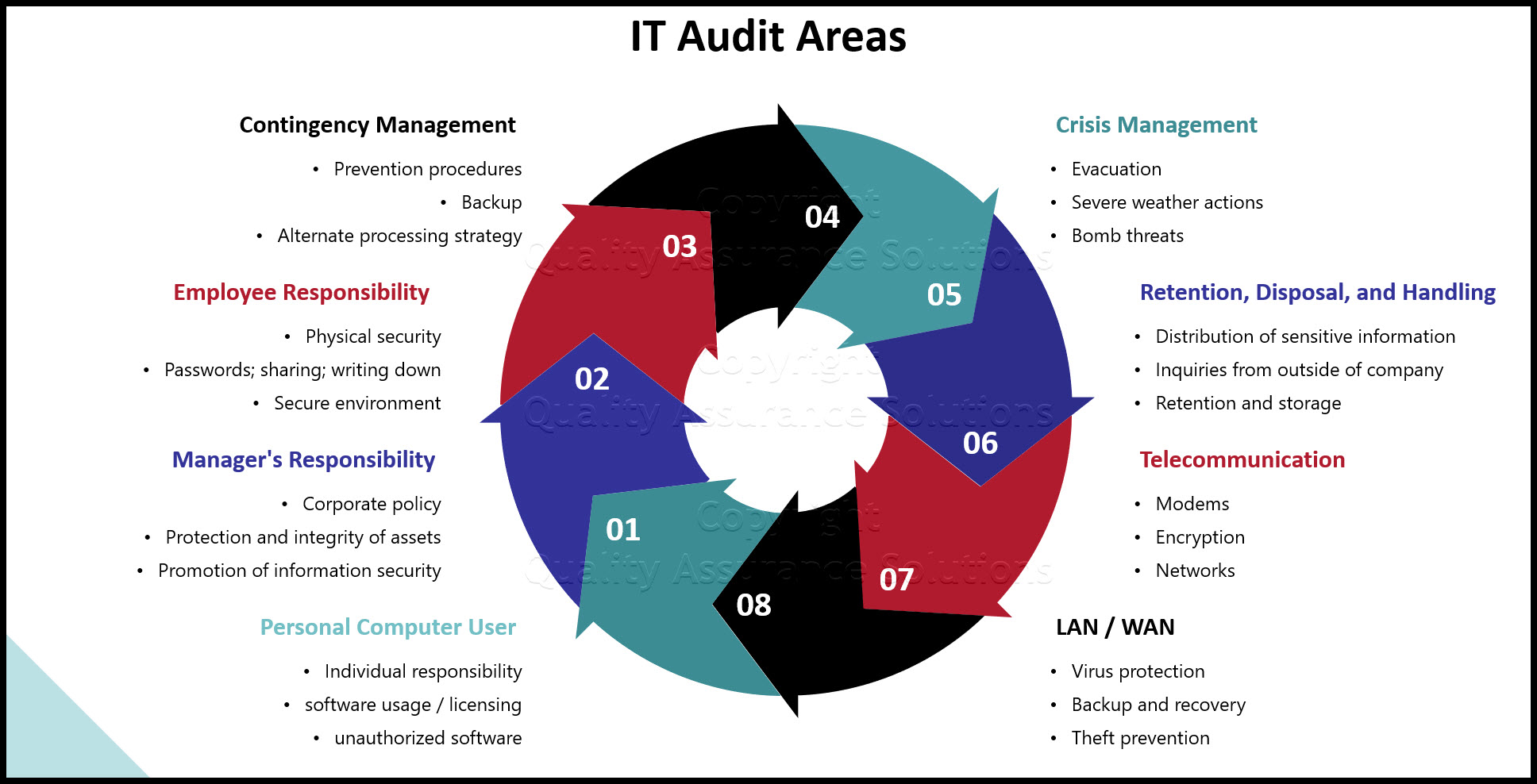
- Procedures for business continuity, including site and application recovery plans, supporting backup and recovery processes, offsite storage, alternate processing strategies, and crisis management plans
- Information retention, archival, and disposal standards and procedures
Get certified in Risk Management through our completely on-line training system. Study at your own pace.
Physical Security
Environment
- Data centers and computer rooms must have good physical security and strong protection from disaster and security threats, whether natural or caused by other reasons, in order to minimize the extent of loss and disruption.
- Backup media containing business essential and/or mission critical information must be housed off-site at a safe distance from the main site in order to avoid damage arising from a disaster at the main site.
Equipment Security
- With the IT audit tool ensure the company places all information systems in a secure environment or attended by staff to prevent unauthorized access.
- Staff in possession of laptop, portable computer, personal digital assistant, or mobile computing devices for business purposes must safeguard the equipment in his/her possession, and must not leave the equipment unattended without proper security measures.
- IT equipment must not be taken off the property without proper control.
Physical Access Control
- A list of persons who are authorized to gain access to data centers, computer rooms or other areas supporting critical activities, where computer equipment and data are located or stored, must be kept up-to-date and be reviewed periodically.
- All access keys, cards, passwords, etc. for entry to any of the computer systems and networks must be physically secured or subject to well-defined and strictly enforced security procedures.
- All visitors to data centers or computer rooms must be monitored at all times by an authorized person.
- For this IT Audit Tool and Guide look to make sure automatic protection features (e.g. password protected screen saver, keyboard lock) in servers, computer terminals, workstations or microcomputers are activated if there has been no activity for a predefined period of time. This prevents an illegal system access attempt. Alternatively, the logon session and connection should be terminated. Also, user workstations should be switched off, if appropriate, before leaving work for the day or before a prolonged period of inactivity.
- All staff with separate personal offices that can be directly accessed from a public area and contain Information System(s) should lock the doors when these offices are not in use.
- The display screen of an Information System on which classified information can be viewed must be carefully positioned so that unauthorized persons cannot readily shoulder-surf.
TrainingKeeper Software. Keep, organize and plan all your employees' training and activities. Software includes multi-user support with reports, certs, and calendars.
Access Control Security
Data Access Control
- Access to information must not be allowed unless authorized by the relevant information owner.
- Data access rights must be granted to users based on a need-to-know basis.
- Data access rights must be clearly defined and reviewed periodically.
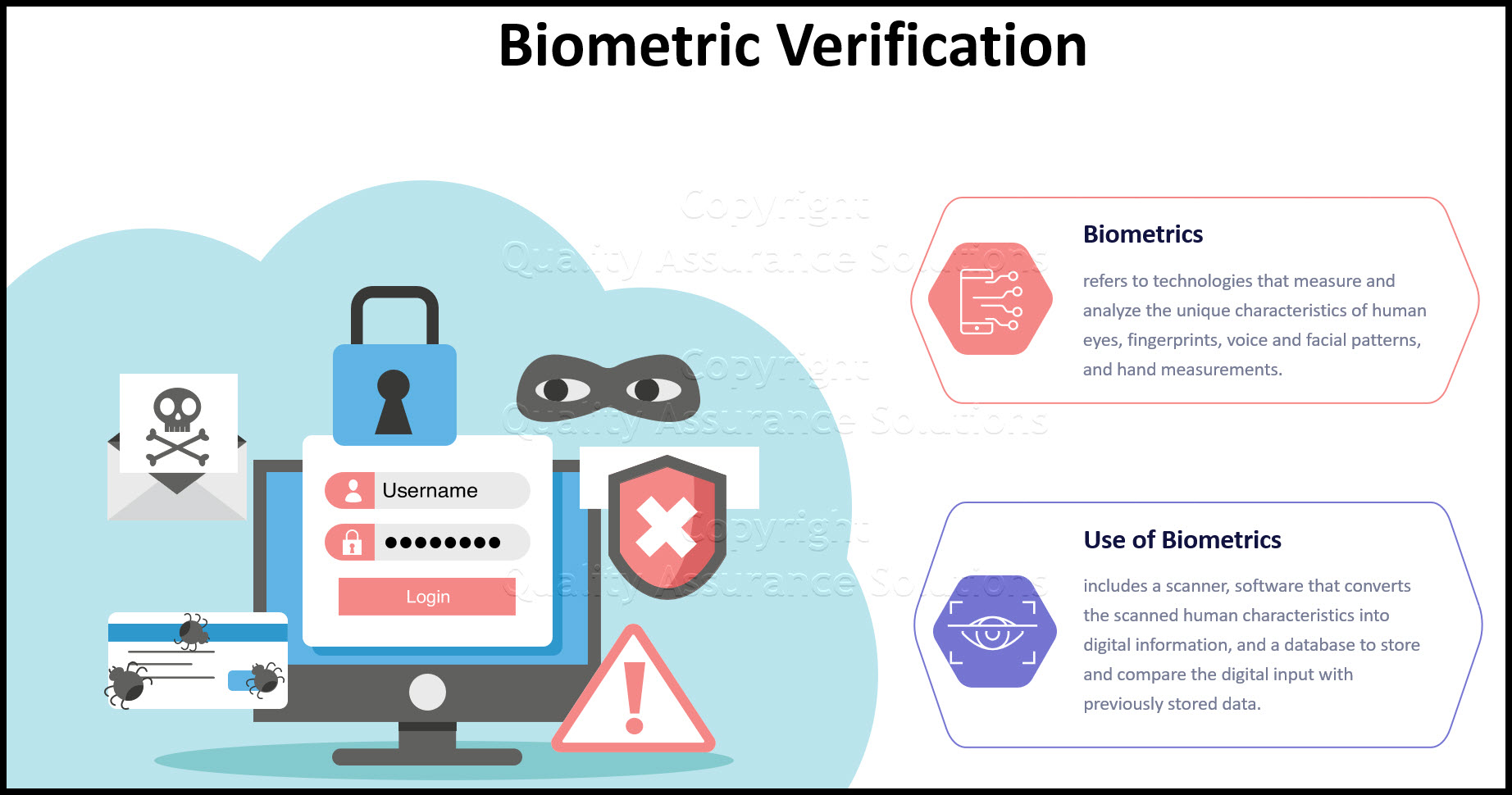
- Access to an Information System containing confidential or classified information must be restricted by means of logical access control.
Authentication
- Access to classified information without appropriate authentication must not be allowed.
- Authentication must be performed in a manner commensurate with the sensitivity of the information to be accessed.
- For this IT audit tool assure the company controls consecutive
unsuccessful log-in attempts.
Privacy
Management reserves the right to examine all information stored in or transmitted by company-owned computer systems.
User Identification
- Each user identity (user-ID) must uniquely identify only one user. Shared or group user-IDs are not permitted unless explicitly approved by the IT Security Officer.
- Users are responsible for all activities performed with their user-IDs.
User Privileges Management
- All accounts must be revoked after a pre-defined period of inactivity.
- For this IT audit tool assure the company periodically reviews user privileges.
- At the time that a member of the staff is transferred or ceases to provide services to the company, all related Information Systems privileges must be promptly terminated.
- The use of special privileges must be restricted and controlled.
8D Manager Software with 5D, 8D, 9D, and RMA report generator. Corrective action software for every company needs.
Password Management
- For this IT audit tool assure the company defines a strict password policy that details at least, minimum password length, initial assignment, restricted words and format, password life cycle, and include guidelines on suitable system and user password selection.
- Passwords must not be shared or divulged unless necessary (e.g., helpdesk assistance, shared PC and shared files). The risk of sharing passwords is that it increases the probability of security being compromised. If passwords must be shared, explicit approval from the IT Security Officer must be obtained. In addition, the shared passwords should be changed promptly when the need no longer exists and should be changed frequently if sharing is required on a regular basis.
- Passwords must always be well protected when held in storage. Passwords must be encrypted when transmitted over an un-trusted communication network. Compensating controls must be applied to reduce the risk exposure of Information Systems to an acceptable level if encryption is not available.
- During IT audit tool assure the company prohibits staff from capturing or otherwise obtaining passwords, decryption keys, or any other access control mechanism, which could permit unauthorized access.
- All vendor-supplied default passwords must be changed before any Information System is put into operation.
- All passwords must be promptly changed if they are suspected of being compromised, or disclosed to vendors for maintenance and support.
Network Access Control
Prior approval from the IT Security Officer is required to connect an Information System with another Information System under the control of another entity. The security level of the Information System being connected must not be downgraded.
Logging
- Business entities must define policies relating to the logging of activities of Information Systems under their control according to the business needs and data classification.
- Within the IT audit tool assure the company keeps logs that provide sufficient information to support comprehensive audits of the effectiveness of, and compliance of security measures.
- Logs must be retained for a period commensurate with their usefulness as an audit tool. During this period, such logs must be secured such that they cannot be modified, and can only be read by authorized persons.
- Logs must not be used to profile the activity of a particular user unless it relates to a necessary audit activity supported by the IT Security Officer.
- Regular checking on log records, especially on system/application where classified information is processed/stored, must be performed, not only on the completeness but also the integrity of the log records. All system and application errors which are suspected to be triggered as a result of security breaches must be reported and logged.
- Clock synchronization should be configured to keep the clocks of Information Systems in sync.

Data Security
Overall Data Confidentiality
- Information about Information Systems that may compromise the security of those systems must not be disclosed to users, or any other third parties, except on a need-to-know basis and only if authorized by the IT Security Officer.
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company's staff must not disclose information about the individuals, business entities or specific systems that have suffered from damages caused by computer crimes and computer abuses, or the specific methods used to exploit certain system vulnerabilities, to any people other than those who are handling the incident and responsible for the security of such systems, or authorized investigators involved in the investigation of the crime or abuse.
- Staff must not disclose to any unauthorized persons the nature and location of the Information Systems, and the information system controls that are in use or the way in which they are implemented.
- All stored information classified as confidential or above must be encrypted.
- Business entities must comply with handling in relation to Information Systems security including, but not limited to, storage, transmission, processing, and destruction of classified information.
Information Backup
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company's backup and recovery procedures are well documented, properly implemented, and tested periodically.
- Backups must be carried out at regular intervals.
- Backup activities must be reviewed regularly.
- Backups must be stored off-site at a remote distance from the main site, and be protected. Backup media should also be protected against unauthorized access, misuse, or corruption during transportation.
PDCA Complete is an organizational task management system with built-in continuous improvement tools. Includes projects, meetings, audits and more.
Built by Quality Assurance Solutions.
Application Security
Application Development & Maintenance
- Application development staff must include security planning and implement the appropriate security measures and controls for systems under development according to the systems' security requirements.
- Documentation and listings of applications must be properly maintained and restricted on a need-to-know basis.
- For this IT audit tool assure the company, completes and reviews formal testing on the security controls must be performed prior to implementation.
- The integrity of an application must be maintained with appropriate security controls such as version control mechanisms and separation of environments for development, system testing, acceptance testing, and live operation.
- Application development staff must not be permitted to access production information unless necessary.
Configuration Management & Control
- Change control procedures for requesting and approving program/system changes must be documented.
- Changes affecting existing security protection mechanisms must be carefully considered.
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company installs all computer equipment and software under control and audit.
- Business entities must ensure that staffs are formally advised of the impact of security changes and usage on Information Systems.
Your ISO 9001:2015 Kit includes Templates, QA Manual, Implementation Guide and a Gap Assessment Internal Audit Tool for ISO 9001:2015
Network & Communication Security
General Network Protection
- Internal network addresses, configurations and related system or network information must not be publicly released without the approval of the concerned entity.
- All internal networks with connections to other networks or publicly accessible computer networks must be properly protected.
- Security measures must be in place to prevent unauthorized remote access to the systems and data.
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company prohibits staff from connecting workstations to an external network by means of any communication device, such as dial-up modem, wireless interface, or broadband link. Workstations are simultaneously connected to a local area network (LAN) or another internal communication network then approval occurs with the concerned entity.
- Staff must not connect any unauthorized Information System device to an Information System without prior approval as designated by the entity.
- Proper configuration and administration of information / communication systems is required and must be reviewed regularly.
- Connections and links made to other networks must not compromise the security of information processed at another, and vice versa.
- Confidential/Restricted information must be encrypted when transmitted over an un-trusted communication network.
- Top Secret/Secret information must be transmitted only under encryption and inside an isolated LAN approved by the IT Security Officer.
Internet Security
- All Internet access must be either through centrally arranged Internet gateways or the entities own Internet gateway conforming to internal security standards. In circumstances where this is not feasible or having regard to the mode of use, i.e., such modes of use may include, for example, Internet surfing, email exchange, and the use of official, portable computers while on business. The relevant standalone machines must still be protected by any applicable security mechanisms.
- Business entities may consider allowing Internet access through stand-alone machines, provided that there is an approval and control mechanism at an appropriate level within the business entity.
- For this IT audit tool, the company should consider the value versus inconvenience of implementing technologies to blocking non-business web sites. The ability to connect with a specific web site does not in itself imply that users of systems are permitted to visit that site.
- Each entity must clearly define and communicate to users its policy in relation to acceptable Internet usage.
- All software and files downloaded from the Internet must be screened and verified with anti-virus software.
- Staff should not execute mobile code or software downloaded from the Internet unless the code is from a known and trusted source.
This Data Analysis Video teaches you the basic tools for understanding, summarizing, and making future predictions with your collected data. Includes MS Excel templates.
Email Security
- Each entity must clearly define and communicate to users its policy in relation to acceptable email usage.
- Systems administrators must establish and maintain a systematic process for the recording, retention, and destruction of electronic mail messages and accompanying logs.
- Incoming/outgoing email must be screened for computer viruses and malicious codes.
- Internal email address lists containing entries for authorized users must be properly maintained and protected from unauthorized access and modification.
- For this IT audit tool assure the company's email transmission of classified information must be transmitted only on an Information System approved by the IT Security Officer.
- Emails from suspicious sources should not be opened or forwarded.
Protection Against Computer Virus and Malicious Code
- Anti-virus software must always be enabled on all local area network servers and personal computers, and computers connecting to the internal network via remote access.
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company protects their Information Systems from computer viruses and malicious codes. Virus signatures, malicious code definitions as well as their detection and repair engines must be updated regularly and whenever necessary.
- Storage media and files from unknown source or origin must not be used unless the storage media and files have been checked and cleaned for computer viruses and malicious codes.
- Users must not intentionally write, generate, copy, propagate, execute or be involved in introducing computer viruses or malicious codes.
- Business entities must implement proper measures to protect their wireless or mobile computing devices against computer viruses and malicious codes.
Software and Patch Management
- Computers and networks must only run software that comes from trustworthy sources.
- No unauthorized application software must be loaded onto an Information System without prior approval from IT Security Officer as designated by the entity.
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company protects their Information Systems from known vulnerabilities by applying the latest security patches recommended by the product vendors or implementing other compensating security measures.
- Before security patches are applied, proper risk evaluation and testing should be conducted to minimize undesirable effects to Information Systems.
Wireless Security
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company documents, monitors, and controls wireless networks with connection to internal networks.
- Proper authentication and encryption security controls must be employed to protect data communication over wireless networks with connection to internal networks.
Learn SPC in an hour. Train your employees. Improve your processes and products. Prevent defects and save your company money.
Security Risk Assessments & Audits
Security Risk Assessment
- Information Systems security risk assessments for information systems and production applications must be performed at least once every two years. A security risk assessment must also be performed prior to major enhancements and changes associated with these systems or applications.
- Use of software and programs for security risk assessment analysis must be restricted and controlled.
Security Auditing
- Information Systems must be periodically evaluated by auditors of an independent and trusted party to determine the minimum set of controls required to reduce risk to an acceptable level.
- Auditing of compliance of computer and network security policies must be performed periodically.
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company use of software and programs for security audit analysis must be restricted and controlled.
Security Incident Management
Security Incident Monitoring
- Business entities must establish an incident detection and monitoring mechanism to detect, contain and ultimately prevent security incidents.
- For this IT audit tool, assure the company ensures that system logs and other supporting information are retained for the proof and tracing of security incidents.
Security Incident Response
- For this IT audit tool assure the company establishes, documents and maintains a security incident handling/reporting procedure for their Information Systems.
- Staff must be made aware of the security incident handling/reporting procedure that is in place and must observe and follow it accordingly.
- All network or systems software malfunctions, information security alerts, warnings, suspected vulnerabilities, and the like, and suspected network security problems, must be reported immediately only to the responsible party according to the incident handling procedure.
- Immediate follow-up actions are required on suspected system intrusion according to security incident handling/reporting procedures.

What To Do Prior To An Audit
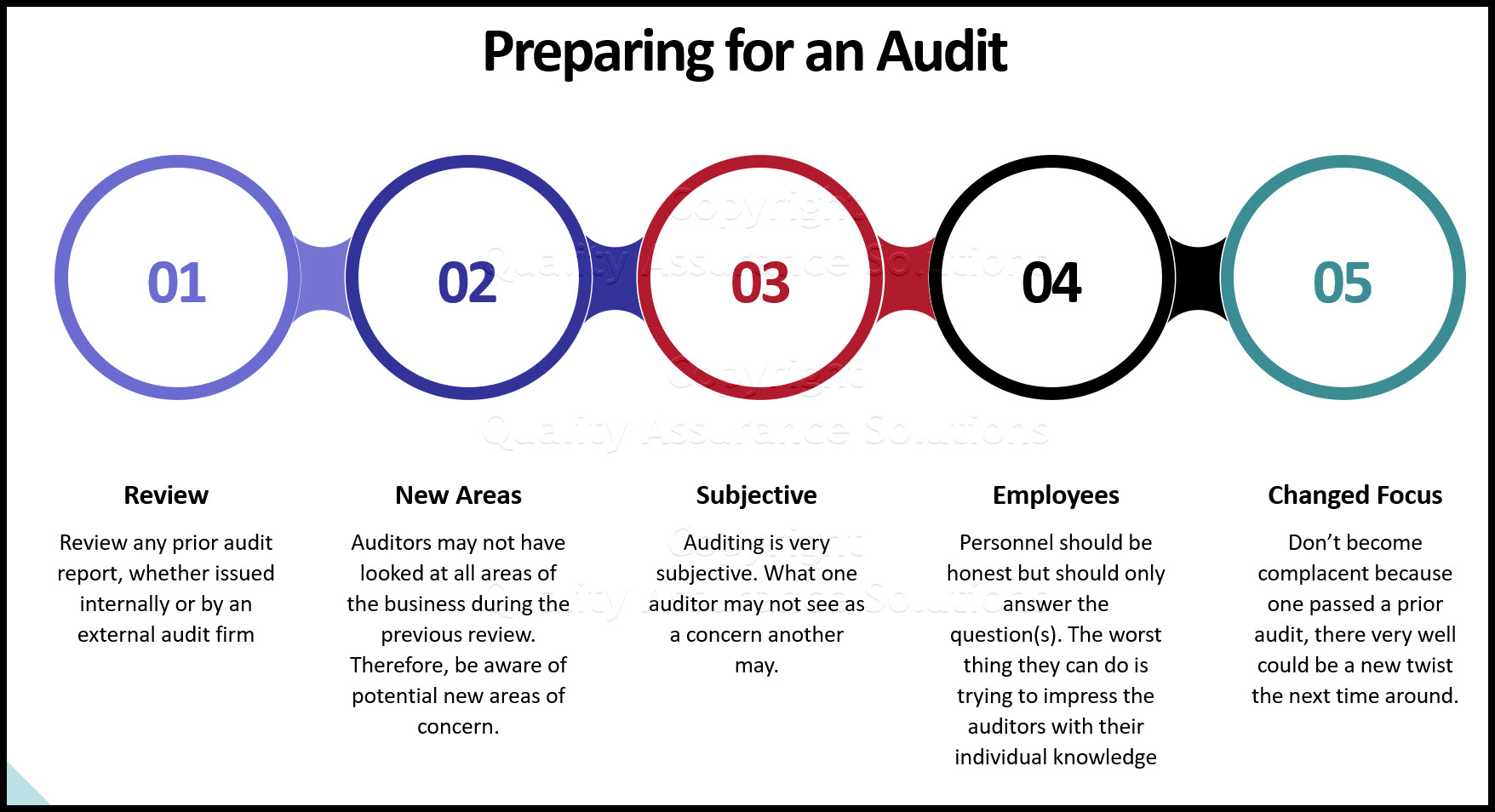
Review Prior Audit Documentation
Always review any prior audit report, whether issued internally or by an external audit firm, and ensure that any actions to be taken/plans to be implemented have indeed been accomplished. Auditors usually start an engagement by looking for prior audit reports, and associated prior audit comments (they usually have copies on file). If they exist (prior reports and prior comments), and if they haven’t been addressed, more than likely a "repeat comment" will be written. This is probably one of the worst things that can happen from the eyes of one’s executive leadership team. Their perception of this condition is that "sound business practices" are either not in place, are very loose, or focus is very weak. This situation usually results in either a management change and/or a reprimand.
Auditors may not have looked at all areas of the business during the previous review. Therefore, be aware of potential new areas of concern that one may have overlooked. Auditors keep extensive work papers on each audit for use by other audit personnel. Just because there is a different audit crew doesn’t mean they're not aware of any prior concerns.
Auditing is very subjective. What one auditor may not see as a concern another may, that’s just the way it is.
The Auditor-In-Charge sets the real tone of the audit. Find out who that is and observe them closely.
IT audit tool and guides are continually updated for technology. During auditor office time, auditors are generally assigned a subject to review and update accordingly. Therefore, don’t become complacent because one passed a prior audit, there very well could be a new twist the next time around.
A smart auditor never asks a question that he/she doesn't already know the answer to, or have a fairly good idea what it should be.
Well-meaning employees can be the worst enemy during an audit while having all the right intentions. Personnel should be honest, but should only answer the question(s) they are asked. The worst thing they can do is to try to impress the auditors with their individual knowledge, or try to answer a question when they’re not qualified to do so. Auditing experience has shown that 15% to 20% of audit comments come from employees making voluntary statements during idle conversation with an auditor.
The role of the local coordinator is crucial in monitoring the auditor’s activities; maintaining records of exhibits; sitting in on auditor interviews to ensure that scope creep is not occurring. At a minimum, a focal point such as this will give one the perception that one’s company or one’s department is in control.
Comprehensive ISO 9001:2015 Audit Checklist for Internal, Gap and Certification Audits.
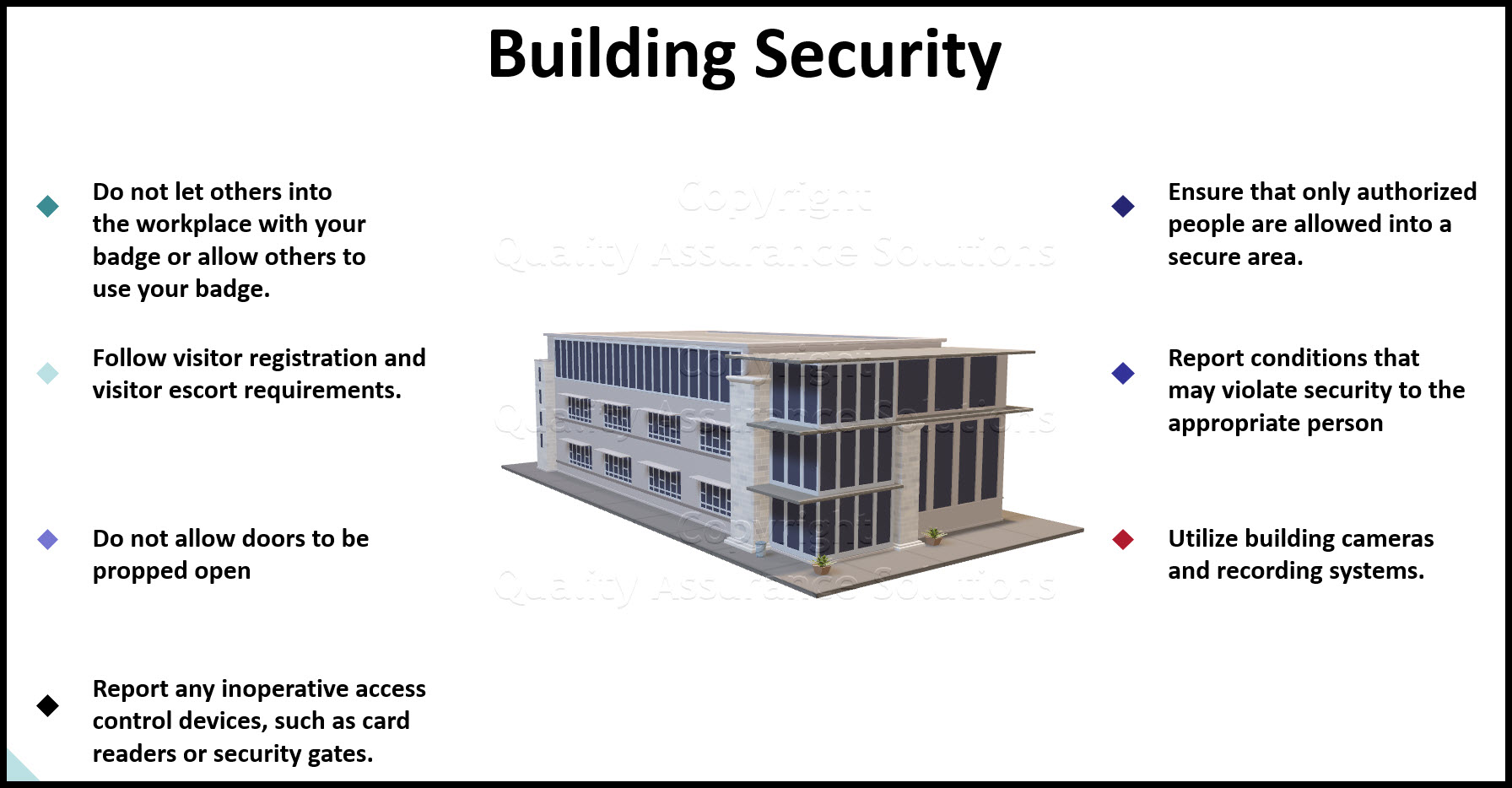
Ensure Computer Rooms, Phone Closets, and Communication Hub Rooms are Secured
- Maintain a list of who has access to the rooms.
- Maintain a record of key holders and combination door lock changes.
- Changes are to be made whenever an employee who had access leaves or no longer requires access.
- Emergency fire equipment must be located in a conspicuous place and properly labeled.
- If it applies, a false floor puller must be mounted in a clear accessible location and labeled.
- Be sure evacuation plans are posted and not obscured.
Example Musts
Signed on terminals should not be left unattended.
Passwords should be hard to guess, i.e., not spouse or children’s names.
Passwords should be a minimum of 8 characters, and changed every 30 days.
Passwords can not be shared.
Printed material should be secured to the same degree it is secured in the computer.
Hard copy should be removed from the printer as soon as it is printed, if at all sensitive or confidential.
In the case of an employee termination or transfer, all computer access must be terminated swiftly.
Digital media should be secured when not in use if they contain proprietary, confidential, or sensitive information.
Digital media should be backed up regularly if they contain information expensive to replace, periodically otherwise.
A disaster recovery plan should be documented and kept off-site along with the most current system backup media.
For this IT audit tool, the use of company resources for personal use must be explicitly pre-authorized in writing by management.Your on-line Lean Six Sigma Certification. Course includes videos, reference materials, mobile app, quizzes and a certification test. Start studying today and get certified at your own pace.
What To Do During An Audit
Ensure computer rooms, phone closets, and communication hub rooms remain secured.
Sign auditors in and out as visitors.
Do not allow auditors free access to restricted areas; escort them.
Give the auditors a tour of the area and acquaint them with the facilities such as phones, restrooms, coffee area, vending machines, cafeteria, evacuation routes, etc. Introduce them to the appropriate personnel.
Always be courteous to the auditors, not overly friendly, but polite.
Be sure that all meeting attendees (there are usually kick-off, fact-finding, agreement-in-fact, and closing meetings) are punctual (meetings are usually pre-arranged), attentive, prepared, and bring all requested deliverables.
Provide only what has been requested for each meeting.
Maintain a log of exhibits turned over to the auditors.
For this IT audit tool, answer only the questions that are asked, and never volunteer information or try to impress the auditors.
Keep informal conversations to a minimum and do not joke around. If one does not know the answer to a question, seek out those individuals who do know; do not guess or attempt to bluff.
If problems or major disagreements occur, do not get into a confrontational situation with the auditors. Be sure to engage the appropriate management team.
If there are compensating controls that have been instituted, be sure to mention them during discussions of that, and only that, particular issue.
Attempt to fix audit findings while the audit is in progress and document what one did to fix the concern; be specific. It is important that the local staff fully understand why a comment was written, and what measures are/were required to implement the necessary controls.
Refrain from buying the auditor’s soft drinks, lunches, or encouraging after hours associations. Avoid any occurrence of impropriety between the local staff, audit personnel, customers, etc.
|
Quality Assurance Solutions Robert Broughton (805) 419-3344 USA |
 |
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications | ||
|
An Organizational Task Management System. Projects, Meetings, Audits & more | ||
|
Corrective Action Software | ||
|
Plan and Track Training | ||
|
AQL Inspection Software |
|
450+ Editable Slides with support links | ||
|
Learn and Train TRIZ | ||
|
Editable Template | ||
|
Templates, Guides, QA Manual, Audit Checklists | ||
|
EMS Manual, Procedures, Forms, Examples, Audits, Videos | ||
|
On-Line Accredited Certifications Six Sigma, Risk Management, SCRUM | ||
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications |