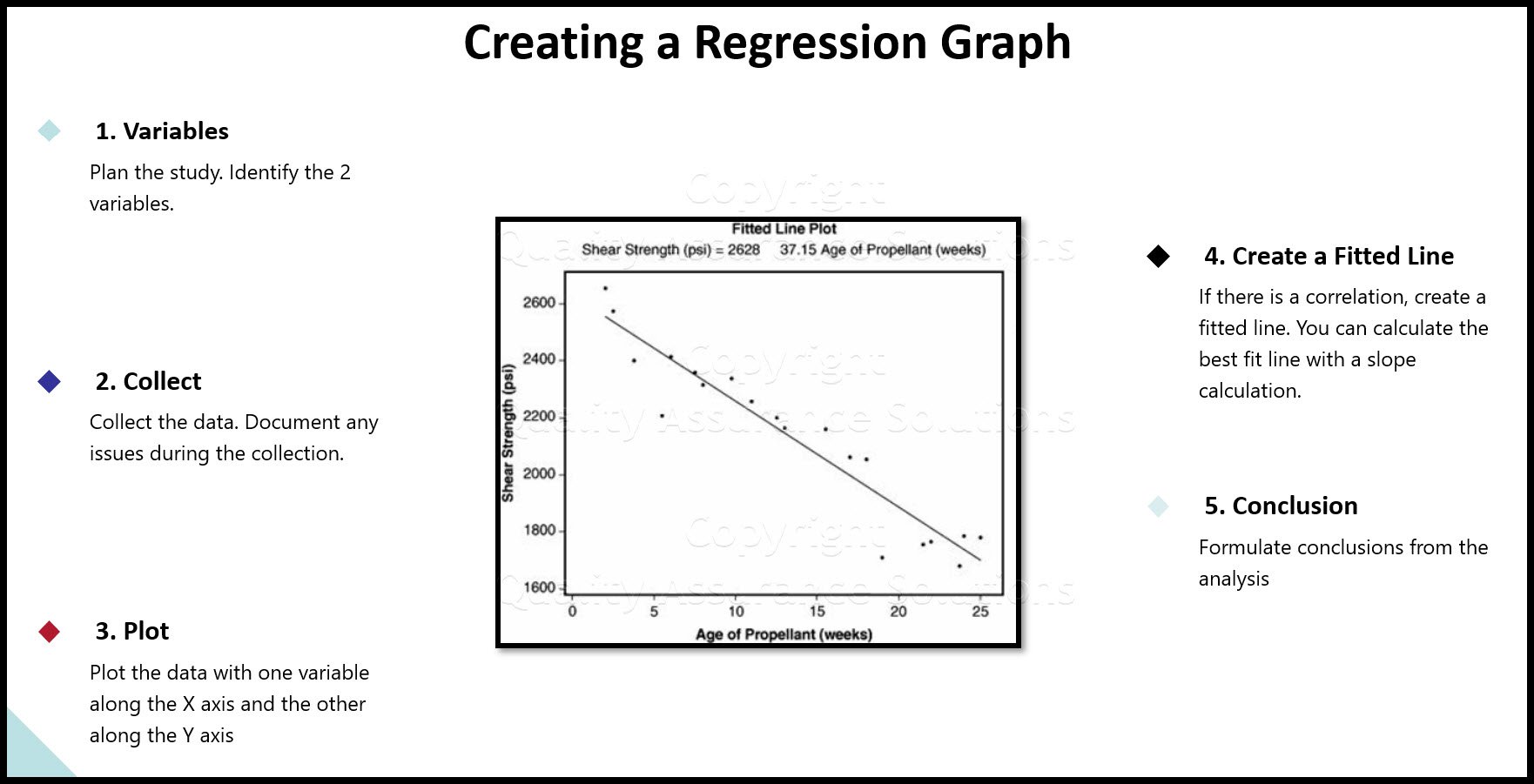
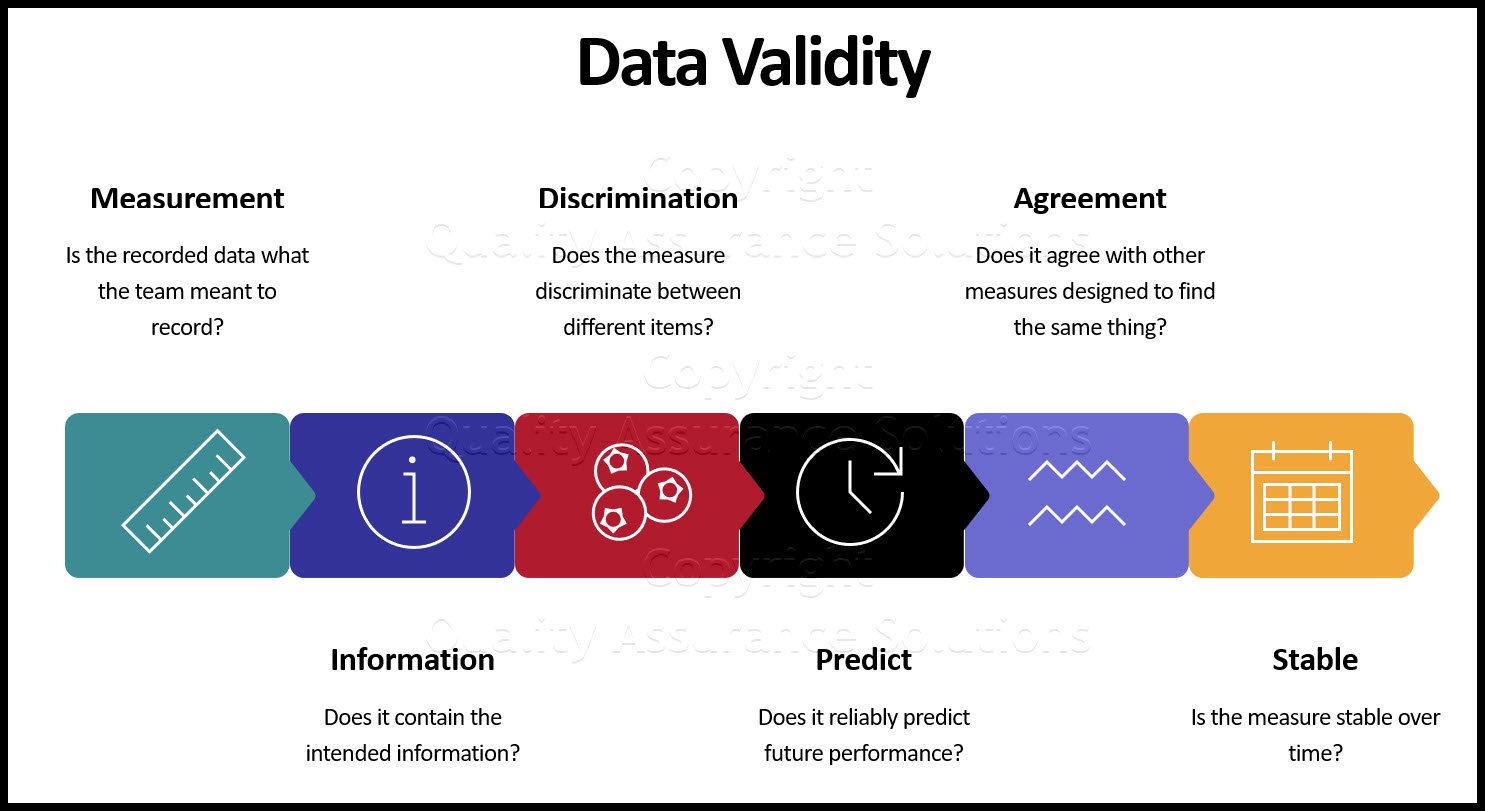
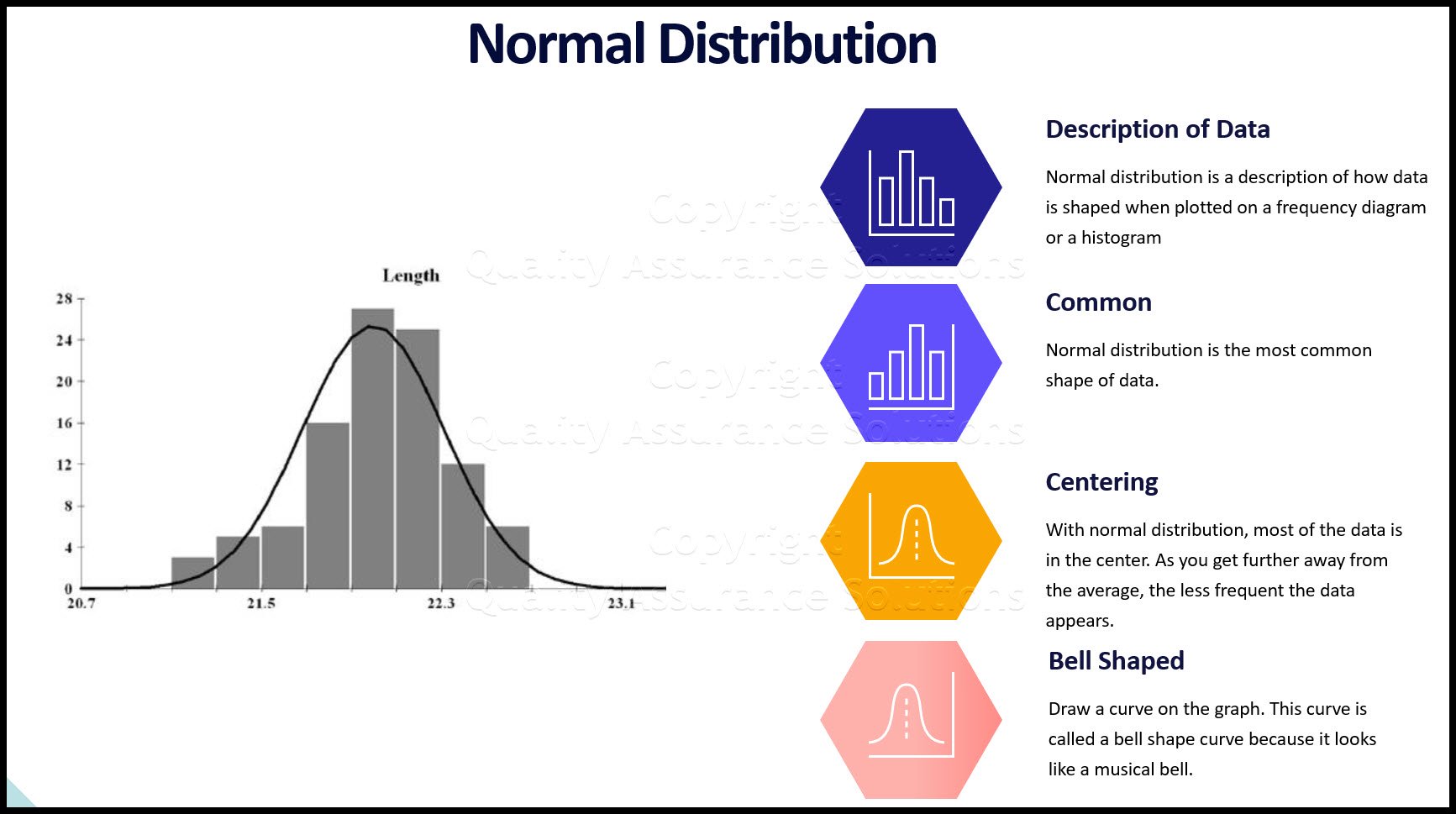
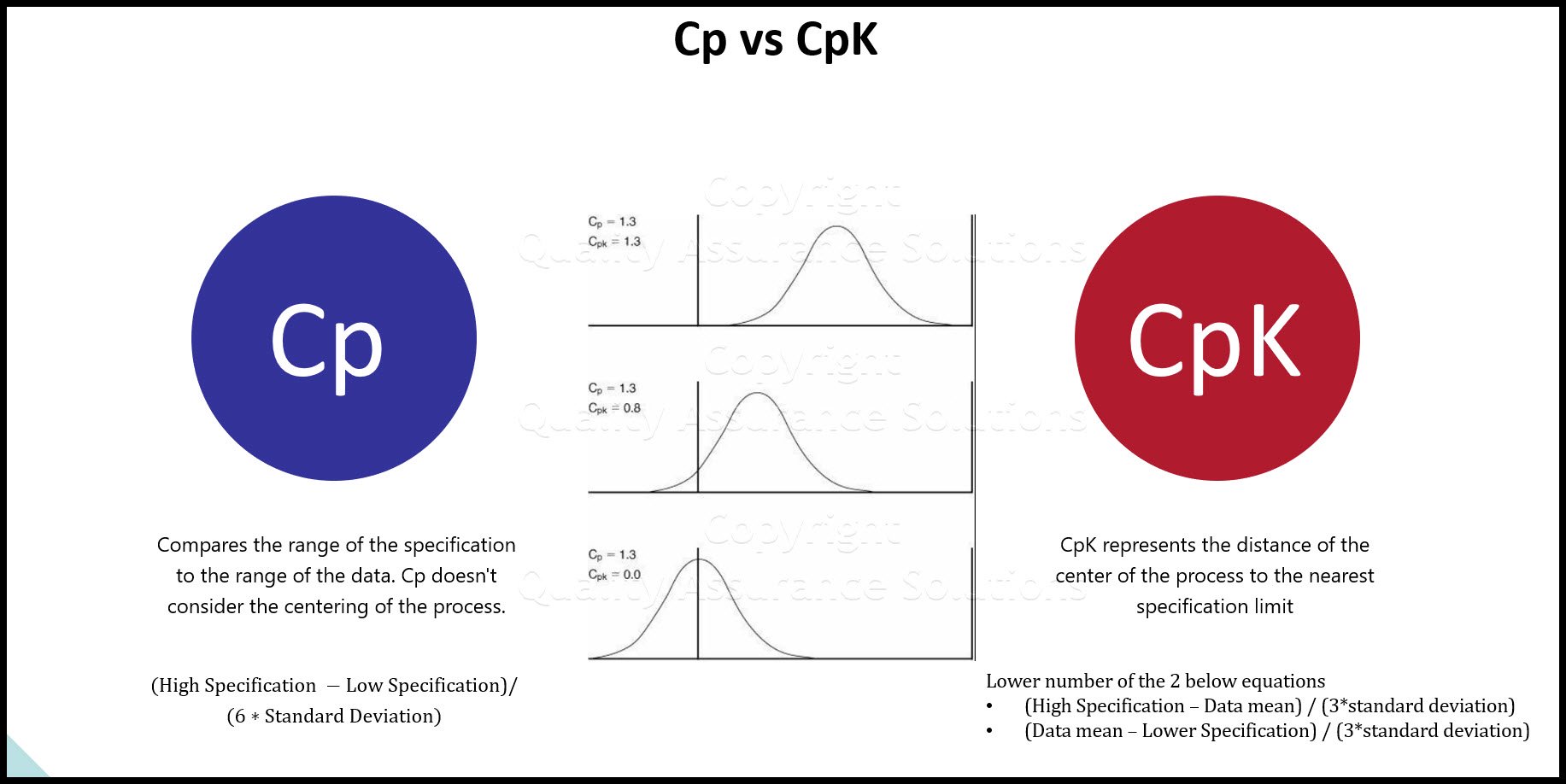
Process Capability Studies
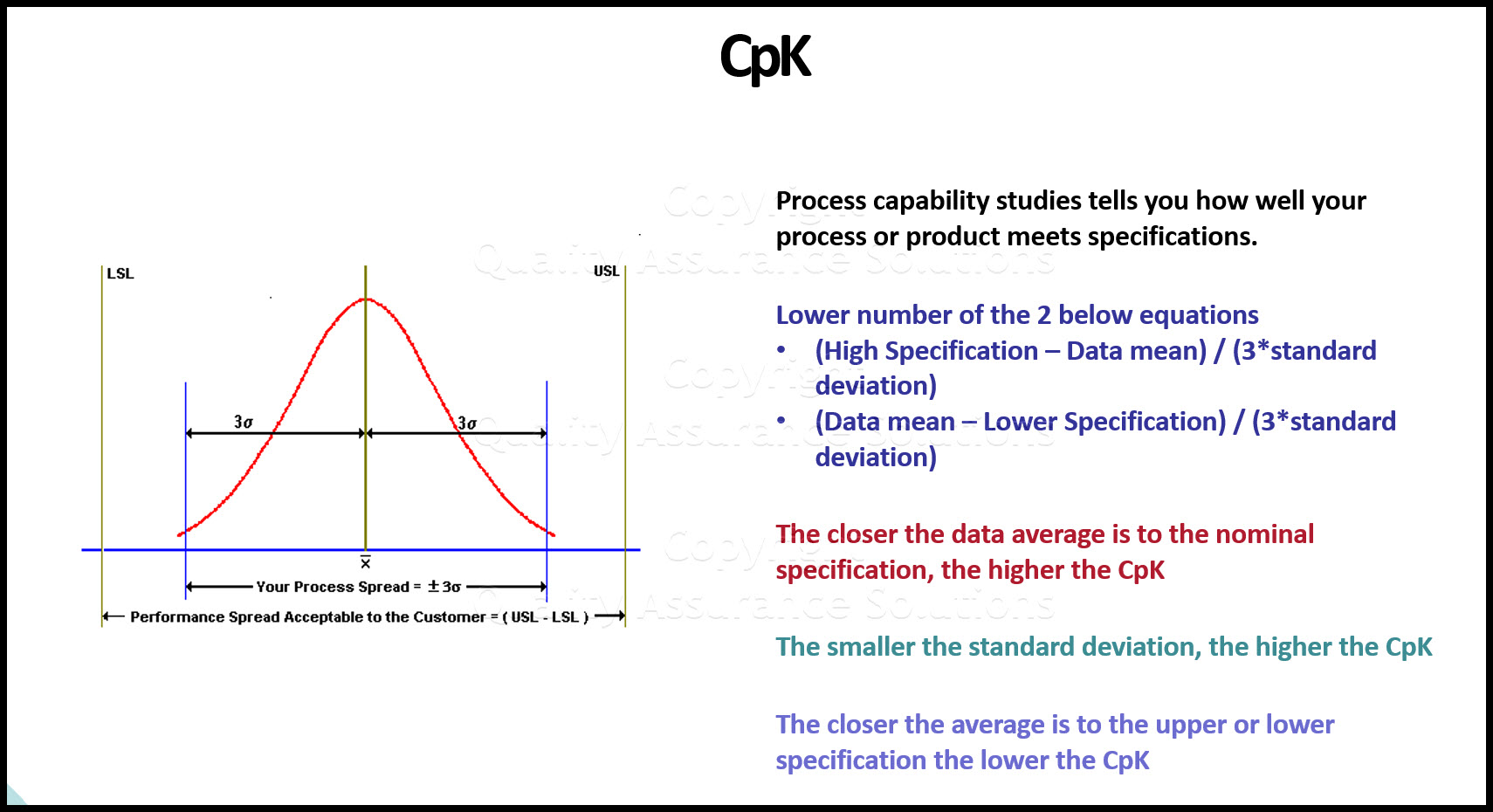
Process capability studies tells you how well your process or product meets specifications. Process capability baseline numbers predicts current and future defects for any given measurement characteristic.
The term for process capability is CpK.
This Data Analysis Video teaches you the basic tools for understanding, summarizing, and making future predictions with your collected data. Includes MS Excel templates.
CpK Guidelines
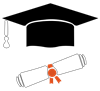
- Have at least 30 measurements
- Assure the data is normally distributed
- Use sample standard deviation
- Be sure to calculate on both upper and lower specification
CpK Calculation Elements
Easy to calculate process capability if you have these 3 items:
- mean
- standard deviation
- specification limits
This Data Analysis Video teaches you the basic tools for understanding, summarizing, and making future predictions with your collected data. Includes MS Excel templates.
CpK Equation for Process Capability Studies
Lower number of the 2 below equations
(High Specification – Data mean) / (3*standard deviation)
or
(Data mean – Lower Specification) / (3*standard deviation)
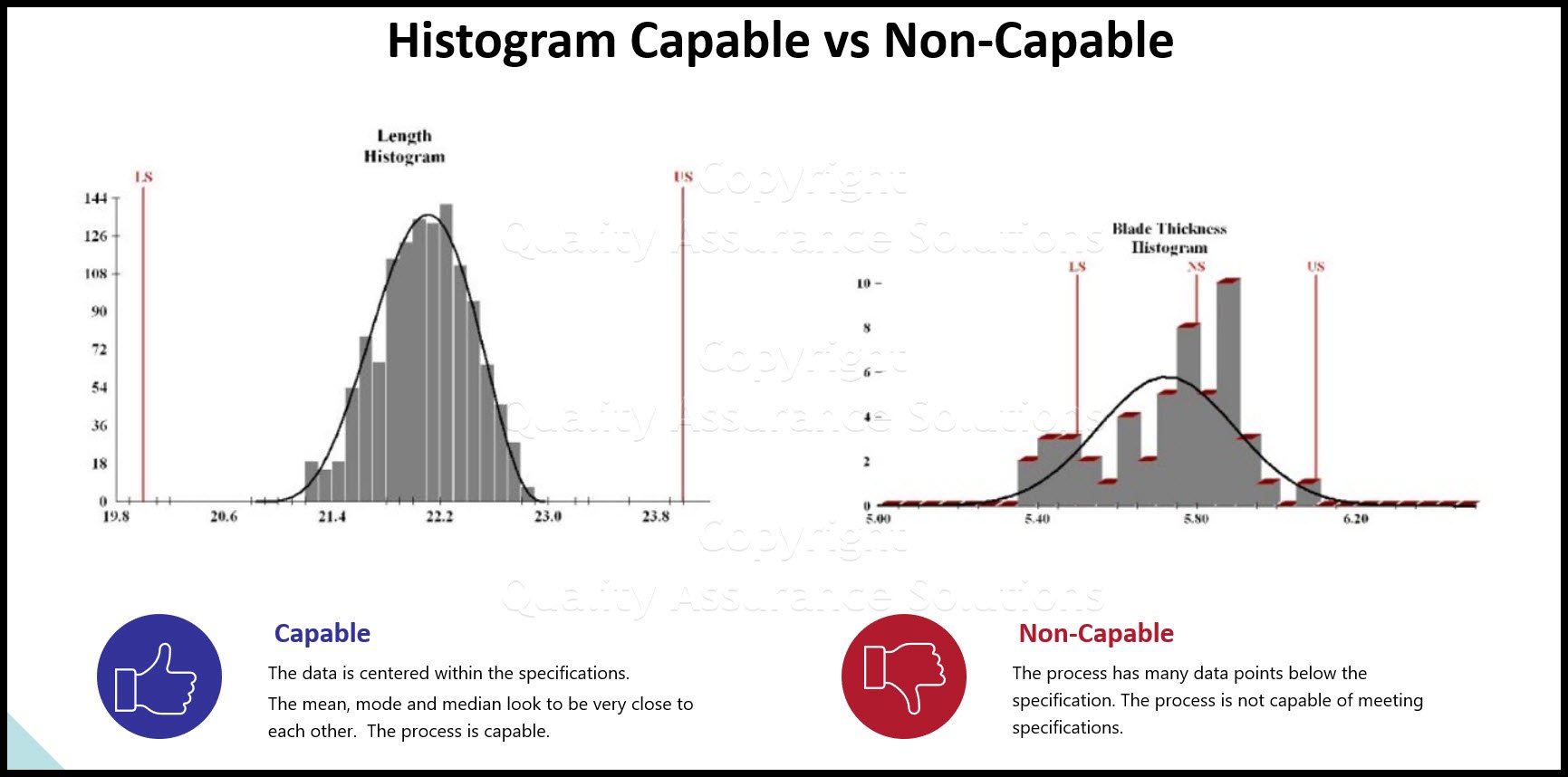
CpK Interpretation
- The closer the data average is to the nominal specification, the higher the CpK.
- The smaller the standard deviation, the higher the CpK
- The closer the average is to the upper or lower specification the lower the CpK
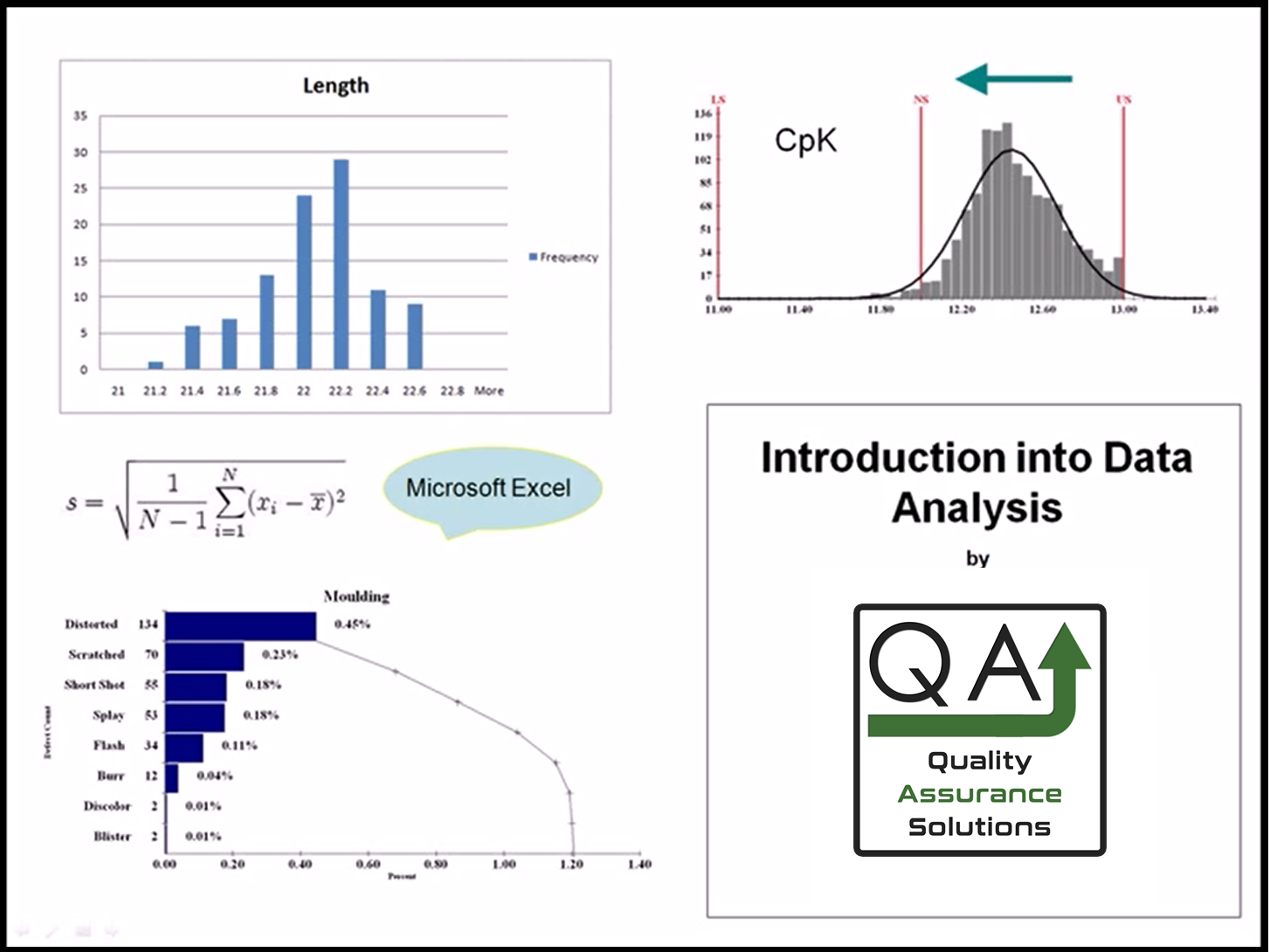
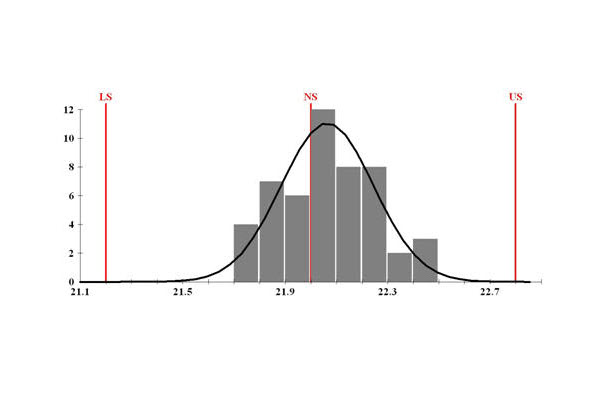
Process Capability and Defects.
Definition of a defect: When a part is beyond the specification, the part is consider a defect.
See the below table for calculation of defects per million parts after calculating the CpK. This is the results of process capability studies.
This Data Analysis Video teaches you the basic tools for understanding, summarizing, and making future predictions with your collected data. Includes MS Excel templates.
Attribute Capability
Capability is just one of the many performance metrics available in six
sigma metrics. Others include throughput, Overall Equipment
Effectiveness, cycle-time, and so on. It comes in two forms
which depends on your type of data , variable and attribute. Both look
at performance versus specification(s). Here we focus on the application
of attribute type data. For a detail look at variable data then please
visit this page.
DPU
Attribute capability is expressed as Defects per Unit (DPU), calculated as:
It is necessary, therefore, to define the unit and the defect. A unit
is the physical output from the process. It is something that is
inspected, evaluated, or judged to determine suitability for use. It is
something delivered to customers or users. Examples include:
- Invoice
- Shipment
- Customer
- CallOrder
A defect is anything that does not meet a critical customer requirement or an established standard. Examples include
- Typographical error on an invoice
- Incomplete shipment
- Customer call dropped
- Missing order information
There can be multiple defect types for each unit and multiple defects
of each type per unit. When evaluating DPU, you decide on the
definition. DPU could mean the total of all the individual defects (or
errors) on each unit. Or it can be applied to individual defect types,
thus identifying which defect type is creates the largest loss.You can
count defects per unit, or count units defective.
You generally use attributes to identify opportunities by prioritizing based on the commonest defect type (typically using a Pareto Chart).
- QAS Home
- CpK
|
Quality Assurance Solutions Robert Broughton (805) 419-3344 USA |
 |
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications | ||
|
An Organizational Task Management System. Projects, Meetings, Audits & more | ||
|
Corrective Action Software | ||
|
Plan and Track Training | ||
|
AQL Inspection Software |
|
450+ Editable Slides with support links | ||
|
Learn and Train TRIZ | ||
|
Editable Template | ||
|
Templates, Guides, QA Manual, Audit Checklists | ||
|
EMS Manual, Procedures, Forms, Examples, Audits, Videos | ||
|
On-Line Accredited Certifications Six Sigma, Risk Management, SCRUM | ||
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications |