Root Cause Analysis
Description of Root Cause Analysis
When applying root cause analysis (RCA) you investigate and categorize the root causes of events. The term "event" identifies occurrences that produce or potentially produce these types of consequences.
To develop effective recommendations and solutions you must understand why the event occurred.
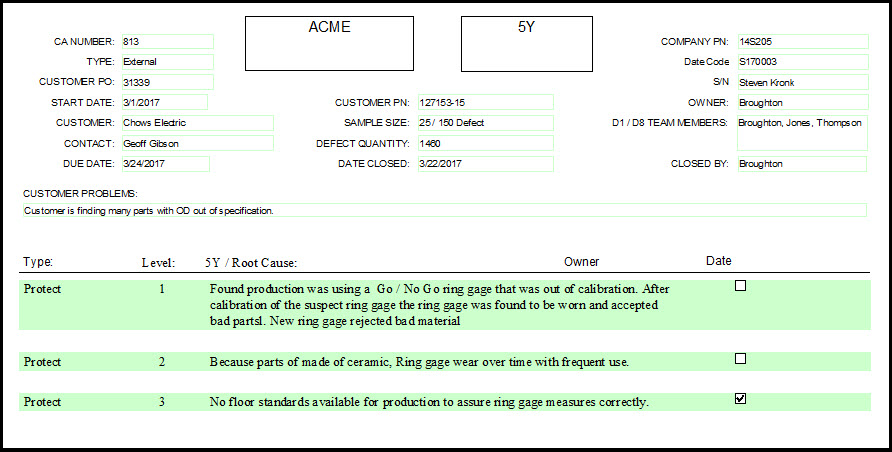
Imagine an occurrence during which an operator is instructed to close valve A; instead, the operator closes valve B. The typical RCA investigation would probably conclude the cause was operator error. However a deeper root cause analyis study may find inadequate training or mislabeled valves.
8D Manager Software with 8D, 9D, 5Y and 4M report generator. Your corrective action software for managing, measuring, and reporting issues.
When To Use
When you want to know the real cause of problem.
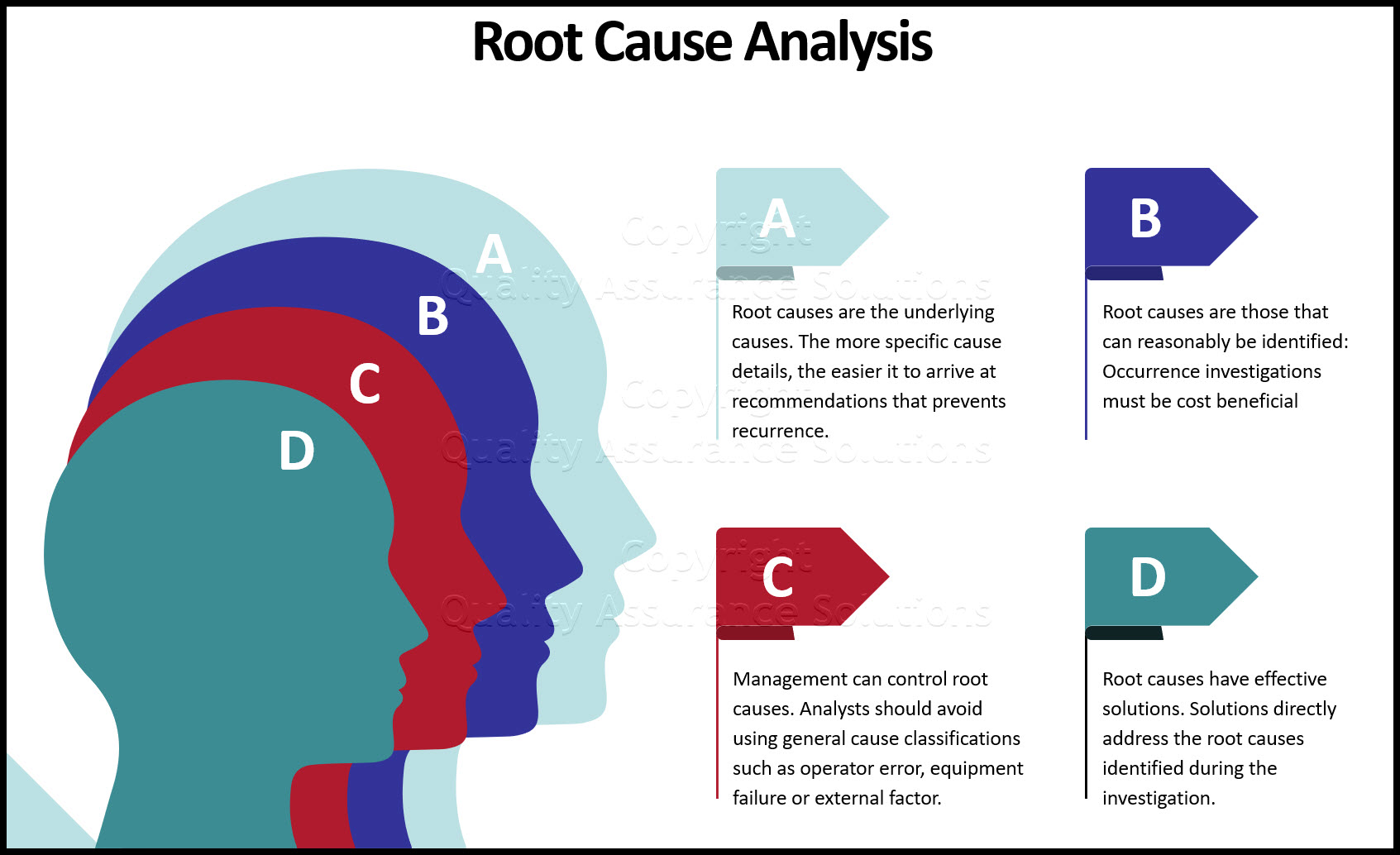
1- Root causes are the underlying causes. The investigator’s goal should be to identify specific underlying causes. The more specific cause details, the easier it to arrive at recommendations that prevents recurrence.
2-Root causes are those that can reasonably be identified: Occurrence investigations must be cost beneficial. It is not practical to keep valuable manpower occupied indefinitely searching for the root causes of occurrences. A structured RCA helps analysts get the most out of their invested investigation time.
3- Management can control root causes. Analysts should avoid using general cause classifications such as operator error, equipment failure or external factor. Why did the operator or machine fail?
4-Root causes have effective solutions. Solutions directly address the root causes identified during the investigation.
Seven Major Steps To Problem Solving:
1. Identify the problem. Utilize a flow chart to imagine the situation and see the location of the problem.
2. List possible root casues. Before jumping to conclusion about the root cause, look at a wide range of possibilities. Fish bone diagram is often used
3. Search out the most likely root cause: Check points might be used to record each failure and supporting information.
4- Identify potential solutions: Here you list all possible solutions arising from Brainstorming.
5- Select and implement a solution. To select the most valuable solution use a Priorities Matrix.
6- Follow up to evaluate the effect. To insure you solved problem, you can use control charts.
7- Standardize the process. Even after solving the problem you need to train employees, update procedures, etc... which ensures every one knows the new solution and procedure.
- QAS Home
- 8D Reports
- Root Cause Analysis
|
Quality Assurance Solutions Robert Broughton (805) 419-3344 USA |
 |
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications | ||
|
450+ Editable Slides with support links | ||
|
Corrective Action Software | ||
|
Plan and Track Training | ||
|
AQL Inspection Software |
|
Learn and Train TRIZ | ||
|
Editable Template | ||
|
Templates, Guides, QA Manual, Audit Checklists | ||
|
EMS Manual, Procedures, Forms, Examples, Audits, Videos | ||
|
On-Line Accredited Certifications Six Sigma, Risk Management, SCRUM | ||
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications |