The Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) helps companies determine specific measurements to balance their financial perspective. BCS enables organizations to clarify their vision and strategy and then translate them into action.
The BSC approach originates from a multi company study conducted during 1990. Researchers believed traditional financial accounting measures were not sufficient to improving businesses. These accounting systems needed to be changed. Representatives from a dozen different organizations (manufacturing, service, heavy industry, and high tech) met bimonthly. They developed a new performance measurement / accounting model. They believed this model would help organizations create future economic value.
Through various iterations and implementation experiences in a variety of organizations, the model evolved to its current format as a strategic management tool. The current BSC accounting requires much more than relying on past performance financial measurements. The company needs a wider measurement system to navigate through the competitive, technological, and capability-driven future.
TrainingKeeper Software. Keep, organize and plan all your employees' training and activities. Software includes multi-user support with reports, certs, and calendars.
How It Works
Essentially, BSC complements financial measures of past performance with additional measures of future performance drivers.
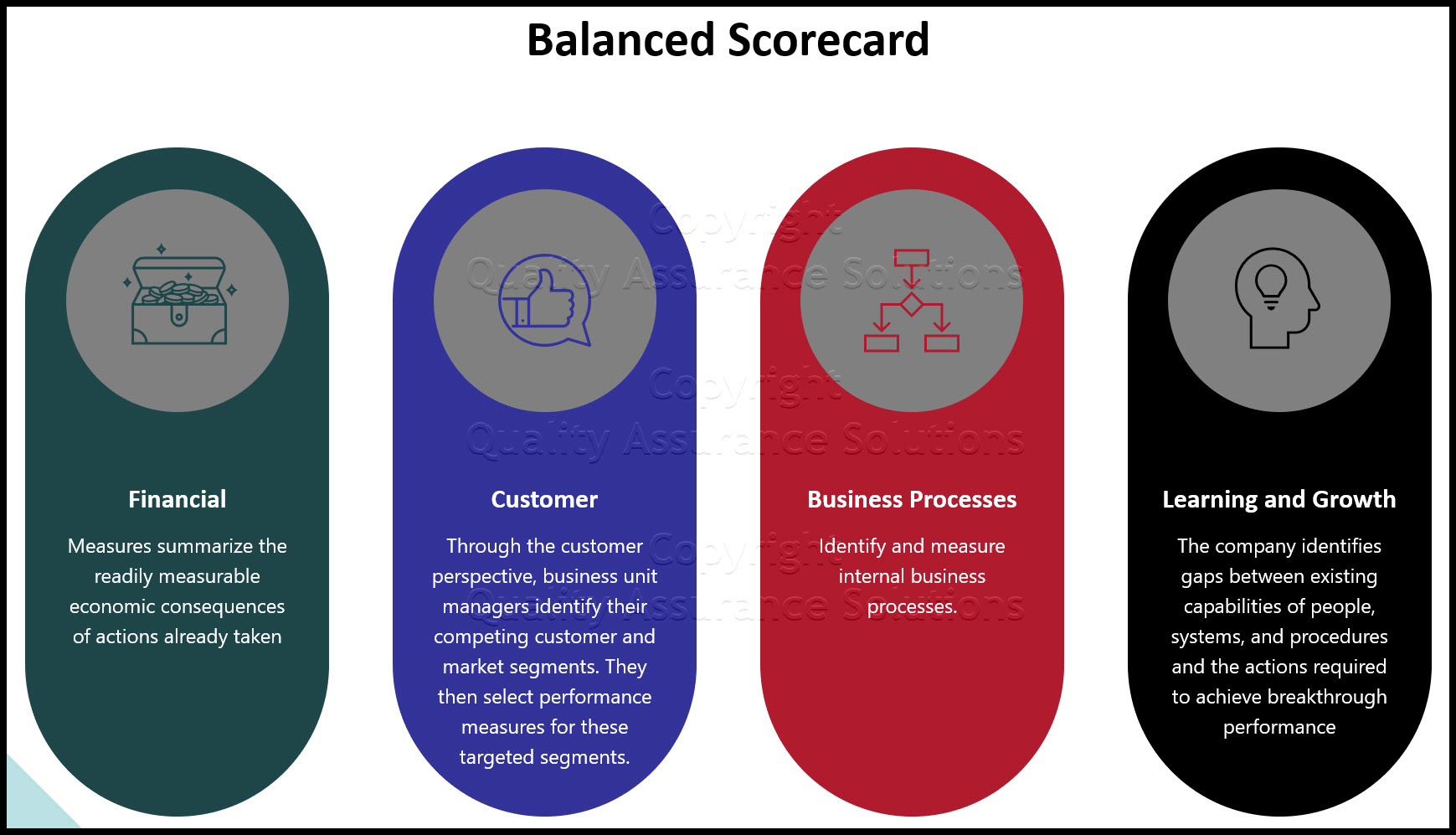
In total, there are four perspectives reflected in the BSC:
1) Financial
2) Customer
3) Internal business processes
4) Learning and growth
The Balanced Scorecard Helps Your Organization Accomplish The Following:
1-Clarify and translate business strategy.
A team of senior executive managers translates business unit strategies into specific strategic objectives. In formulating these objectives, the team clarifies the organizational vision and gains consensus. This team-based step in the BSC creates a shared model for the entire organization.
2- Communicate and link strategic objectives with the measures.
Management communicates the strategic objectives and measures hroughout the company. Communication includes newsletters, bulletin boards, videos, presentations, e-mail, meetings, etc.This tells all employees that strategic objectives must be met for the organizational strategy to succeed. After understanding the high-level objectives for their business units, employees develop local actions to align their units to the stategic objectives.
3- Plan, set targets, and align strategic initiatives.
Senior executives set ambitious targets for the scorecard measures (e.g., ones that would dramatically increase the stock price if the company is public, ones that double the return on investment capital, ones that double the growth rate). Next, managers identify stretch targets for their customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth objectives. Customer satisfaction measures and benchmarking can be used to develop the objectives. Managers then identify all the required initiatives to achieve the strategic breakthrough objectives.
4- Enhance strategic feedback and learning.
This step provides for organizational learning. Monthly and quarterly management reviews examine financial targets as well as the other measures. Monitoring allows adjustments to support business units, or, if necessary, fundamental changes in the strategy.
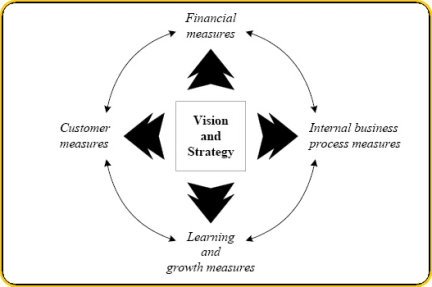
The Four Area Of The Balanced Score Card :
1- Financial perspective:
Financial measures summarize the readily measurable economic consequences of actions already taken. They answer the question: Is the organizations strategy, deployment, and implementation contributing to bottom-line improvement? Examples of financial indicators include:
- Economic value added (EVA).
- Generation of cash flow.
- Operating income.
- Rapid sales growth.
- Return on capital employed.
- Return on net assets (RONA).
2-Customer perspective:
Through the customer perspective, business unit managers identify their competing customer and market segments. They then select performance measures for these targeted segments. Examples of core customer measures are:
- Customer satisfaction.
- Customer retention.
- New customer acquisition.
- Customer profitability.
- Market and account share for the targeted segments.
3- Internal business process perspective:
The internal business process perspective answers the question: What are the critical internal business processes in which the organization must excel? Internal business process measurements enable the business unit to:
-Deliver value propositions that attracts and retain customers in the target market segments.
-Satisfy shareholder expectations of superior financial returns.
The Balanced Scorecard approach usually identifies entirely new processes at which the company must excel to meet customer and financial objectives. The Balanced Scorecard template approach also attempts to incorporate innovation.
4- Learning and growth perspective:
The learning and growth perspective identifies the infrastructure the organization must build to create long-term growth and improvement. The three principal sources of organizational growth and learning are people, systems, and organizational procedures. The company identifies gaps between existing capabilities of people, systems, and procedures and the actions required to achieve breakthrough performance. To close gaps, the organization must invest in re-skilling employees, improving information technology and other support systems, and aligning organizational procedures and routines.
Your ISO 14001 Kit includes Forms, Procedures, EMS Manual, Guidelines, Audits, Examples, Training Material, and Video for your ISO 14001:2015 Implementation
The Value Of Using The Balanced Scorecard
The combining financial and non financial measures is not unique to the Balanced Scorecard method. But in traditional applications, organizations use financial and non financial measures primarily for tactical feedback and control of short-term operations. The Balanced Scorecard provides more than a tactical or operational measurement system.
Innovative organizations use BSC as a strategic management system to manage strategy for long-term benefits. All together, this translates organizational vision and strategy into objectives and measures across a balanced set of perspectives.
In addition to financial measures, the Balanced Scorecard example helps an organization measure...
-How business units create value for current and future customers.
-How internal capabilities must be enhanced.
-What investments must be made in people, systems, and procedures to improve future performance.
|
Quality Assurance Solutions Robert Broughton (805) 419-3344 USA |
 |
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications | ||
|
450+ Editable Slides with support links | ||
|
Corrective Action Software | ||
|
Plan and Track Training | ||
|
AQL Inspection Software |
|
Learn and Train TRIZ | ||
|
Editable Template | ||
|
Templates, Guides, QA Manual, Audit Checklists | ||
|
EMS Manual, Procedures, Forms, Examples, Audits, Videos | ||
|
On-Line Accredited Certifications Six Sigma, Risk Management, SCRUM | ||
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications |